Daily Activities of Elder Adults Using Optimized Deep Learning Model in China
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17762/ijcnis.v15i3.6270Keywords:
Activity of Everyday Living, Chinese Healthy Survey, Category-based Recognition Network, Gazelle Optimization Algorithm, Specific Recognition EncodingAbstract
The health and happiness of seniors can be influenced by the design of public spaces and buildings. Planning for age-friendly communities requires taking into account the wide variety of daily activities and public facility consumption among older persons. Yet, conventional approaches fall short when it comes to providing comprehensive, objective measures of the actions of the elderly. This research proposes an attention-based recognition approach by decomposing neural network outputs into class-dependent features using dictionary learning to improve discrimination performance. This research aimed to develop an empirical typology of activity of daily living (ADL) and its connection to health in China's ageing population. A deep learning-based model was rummaged to categorise the contributors in the Chinese Longitudinal Healthy Longevity Study (CLHLS) into subgroups based on their abilities with ADL. To be more precise, the study trains a category-based recognition network (CRN) by superimposing a basic but effective specific recognition encoding (SRE) unit on top of convolutional layers. In order to encode attention maps for each class, the SRE module uses the feature maps produced by the Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) to learn a class-specific vocabulary. Class-wise adaptive feature refining is achieved by multiplying these attention maps by the input features. In this case, a gazelle optimization algorithm (GOA) handles the hyper-parameter tuning process of the proposed model. This case study is the first of its kind in a dense metropolitan region, and it uses objective measurements to evaluate the activity spaces of the elderly. This research provides empirical data for the promotion of healthy ageing in urban areas.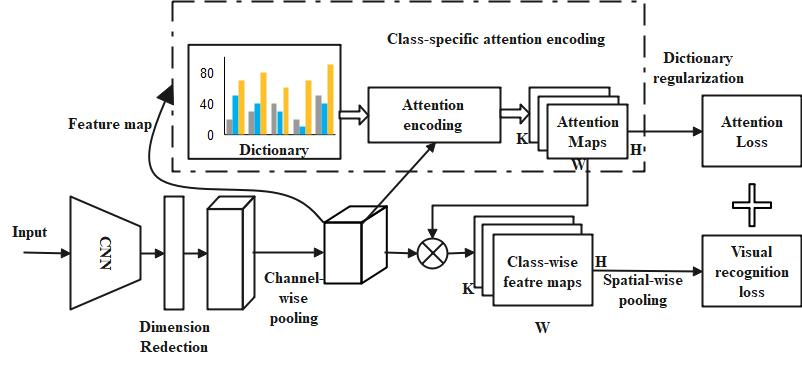
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 International Journal of Communication Networks and Information Security (IJCNIS)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.




