Energy Efficient Clustered Load Balanced LEACH Protocol Based on Particle Swarm Optimization in Underwater Wireless Sensor Networks
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17762/ijcnis.v16i1.6494Keywords:
Base Station (BS), Cluster Head (CH), C-LEACH, E-LEACH, LEACH, Optimization, PSO Algorithm, UWSNAbstract
Underwater wireless sensor networks (UWSN) are generally positioned over a sizeable aquatic area and sensor nodes are mobile due to their distinct environment. The networks' sensor nodes have the ability to self-organize and communicate. The sensor networks are used in many fields, such as habitat monitoring, small energy cost, object/entity tracking, forecasting and remote control of hazardous regions, surveillance, routing etc. Due to their mobility, sensor nodes use more energy, have a lower node distribution density, and require longer localization times. Clustering is an efficient topology control strategy for achieving the goal of conserving energy. This manuscript presents a novel technique for prolonging the lifetime of a network using the LEACH protocol. The proposed load-balanced LEACH protocol uses the concept of PSO (Particle Swarm Optimization) in which a cluster head is chosen based on UWSN's current energy level, load factor, degree of nodes, and distance from the head node are used for clustering to reduce energy consumption. The proposed design has been simulated in NS2.35 and compared with three clustering routing protocols, LEACH, E-LEACH, and C-LEACH on the various performance factors like remaining energy, number of packets transmitted and lost during transmission, bit-rate analysis, number of alive and dead nodes. The proposed design shows an improvement in network lifetime and in energy conservation by selecting optimal cluster heads.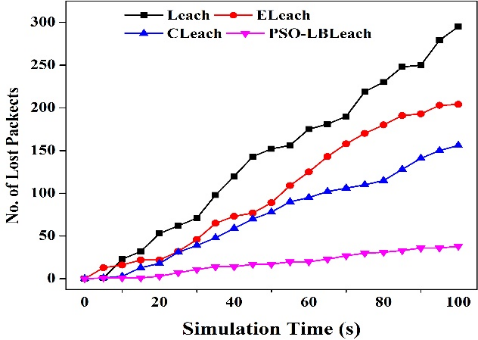
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 International Journal of Communication Networks and Information Security (IJCNIS)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.





