Improving Spectrum Efficiency in 5G Networks via Collaborative Spectrum Sharing for MIMO-NOMA Enhancement
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.17762/ijcnis.v16i2.6570Keywords:
Massive Multiple-Input Multiple-Output, Cooperative cognitive radio networks, Downlink, Dedicated control channels, Quadrature Phase-shift KeyingAbstract
This research utilises two innovative ways to improve the spectrum efficiency of the 5G Downlink Non-Orthogonal Multiple Access (NOMA) power domain. Enhancements are achieved by a Cooperative Cognitive Radio Network (CCRN). Single-Input Single-Output (SISO), Multiple-Input Multiple-Output (MIMO), and Massive Multiple-Input Multiple-Output (M-MIMO) configurations are evaluated within a single cell of a communication network. NOMA users initially compete for CCRN common control channels. NOMA customers are given high-priority dedicated control channels during the second approach. The proposed approaches are assessed using MATLAB for three parameters: distance, power localization coefficient, and transmission power scenarios. Simulation involves four users utilizing 80 MHz bandwidths and Quadrature Phase-Shift Keying (QPSK) modulation. We examine successive interference cancellation and channel instability assuming that Rayleigh signal fades with frequency. User 4 attained the best Spectral efficiency compared to the other four users, achieving 3.9 bps/Hz/cell for SISO Downlink NOMA, 5.1 for CCRN using common channels, and 7.2 for dedicated control channels. The findings were achieved at a transmit power of 40 dBm. User 4, the top performer, attained a spectral efficiency of 51% utilising a 64 x 64 MIMO Downlink NOMA system. At 40 dB transmit power, common control channels and dedicated control channels improved spectral efficiency performance by 64% and 65% respectively compared to SISO Downlink NOMA. Moreover, 128 × 128 M-MIMO Downlink NOMA improved spectral efficiency performance by 79% for the highest-ranked U4 user. When compared to SISO Downlink NOMA at 40 dB transmit power, The CCRN combining common control channels and dedicated control channels improved spectral efficiency performance by 85% and 86%, respectively. According to the study, the second suggested choice, dedicated control channels with Cooperative Cognitive Radio NOMA (CCR-NOMA), provides clients with the maximum spectrum efficiency. MIMO and M-MIMO enhance spectrum efficiency.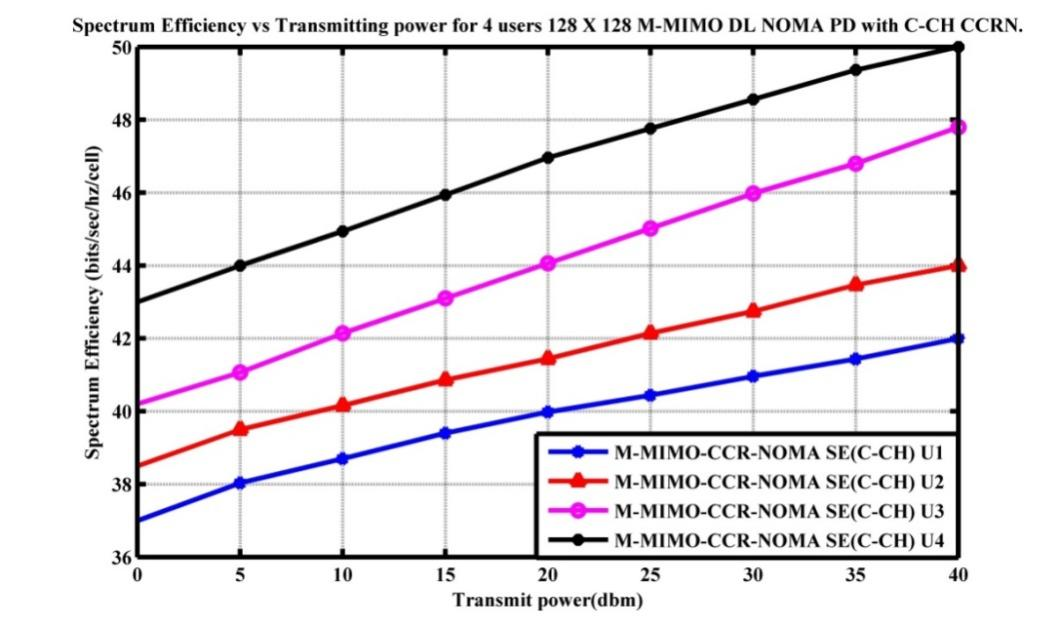
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 International Journal of Communication Networks and Information Security (IJCNIS)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.




